Introduction
Every time you buy a coffee, order a meal, or pick up groceries, you interact with a point of sale (POS). It may look as simple as a cash register or as advanced as a tablet-based system, but behind it lies the technology that powers modern commerce. The point of sale is where a transaction happens between customer and business—where money, data, and products meet.
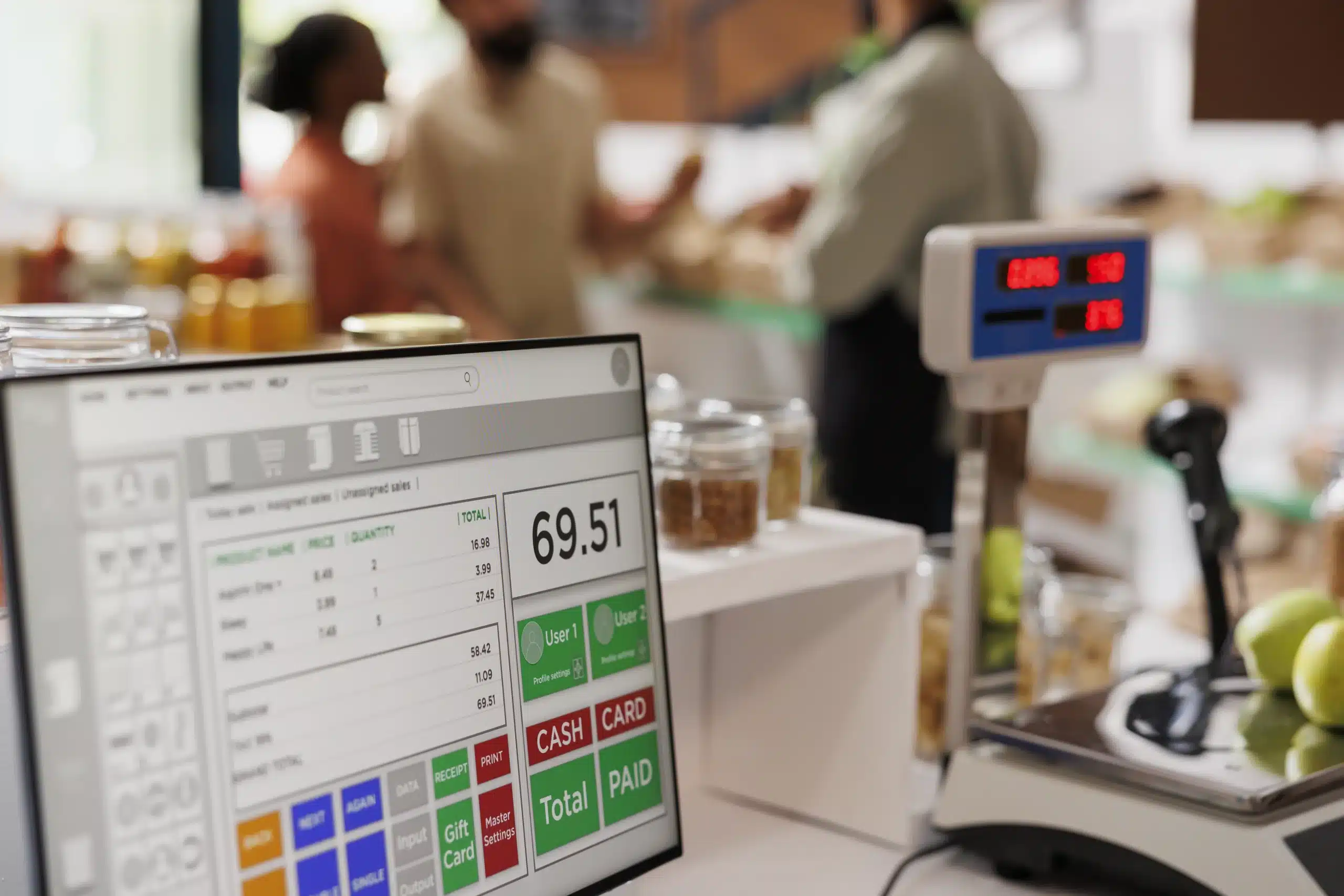

In this guide, we’ll explore what a POS is, how it has evolved, why it matters for businesses, and how to choose the right system. Whether you’re a small shop owner, a restaurant manager, or simply curious about how stores operate, this article will break down the subject in a clear, understandable way.
What Is a Point of Sale?
At its core, the point of sale is the place where a customer pays for goods or services. Traditionally, this was a counter with a cash register. Today, it could be:
-
A touchscreen at a café
-
A handheld device at a food truck
-
A self-service kiosk at a supermarket
-
An online checkout on an e-commerce site
The POS has two layers:
-
The physical location or device where the exchange happens.
-
The software system that records sales, processes payments, and stores transaction data.
This dual function makes POS both a tool for customer service and a backbone for business operations.
A Brief History of the Point of Sale
Understanding the past helps explain the present. POS technology has come a long way in just over a century.
The Mechanical Era
In 1879, James Ritty invented the first mechanical cash register to prevent employee theft in his bar. Early registers simply recorded sales without processing payments.
The Electronic Age
By the mid-20th century, electronic registers appeared. They introduced receipts, calculators, and basic accounting functions.
The Computer Revolution
In the 1970s and 80s, businesses began using POS terminals powered by computers. Restaurants and retail stores could now track inventory and generate sales reports.
The Cloud and Mobile Wave
In the 2000s, POS systems moved to the cloud. This allowed businesses to manage multiple stores, access data in real-time, and use smartphones or tablets as POS terminals.
Today, POS is no longer just a register—it’s an entire ecosystem integrating payments, analytics, and customer management.
Components of a POS System
A modern POS system usually has both hardware and software parts.
Hardware
-
Register or terminal: The main device where transactions are entered.
-
Barcode scanner: Speeds up checkout by scanning product codes.
-
Receipt printer: Provides proof of purchase.
-
Cash drawer: Stores physical money.
-
Card reader or NFC device: Handles digital and contactless payments.
-
Tablet or mobile device: Common in modern cloud-based setups.
Software
-
Sales processing: Records each transaction.
-
Inventory management: Tracks stock levels automatically.
-
Customer relationship management (CRM): Stores customer data and purchase history.
-
Analytics and reporting: Helps business owners understand sales trends.
-
Integrations: Connects with e-commerce, accounting software, or loyalty programs.
Why Businesses Need a POS System
A POS is more than a payment tool. Here are some reasons businesses rely on it:
-
Efficiency – Faster checkout improves customer satisfaction.
-
Accuracy – Reduces human errors in pricing and inventory tracking.
-
Data Insights – Provides real-time reports on sales, profits, and product performance.
-
Inventory Control – Helps avoid stockouts and overstocking.
-
Flexibility – Accepts multiple payment methods: cash, credit cards, mobile wallets, and gift cards.
-
Scalability – Cloud POS systems grow with your business, whether you have one store or many.
For small businesses, a POS can make the difference between running smoothly and drowning in manual work. For larger operations, it’s essential for consistency and control.
Types of POS Systems
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Different businesses use different types of POS systems depending on their needs.
1. On-Premise POS
-
Installed on local servers or computers.
-
Offers stability but requires maintenance and higher upfront costs.
-
Still common in restaurants and large retailers.
2. Cloud-Based POS
-
Runs on the internet, accessible via browser or app.
-
Updates automatically and stores data securely in the cloud.
-
Popular among small to mid-sized businesses due to affordability.
3. Mobile POS (mPOS)
-
Operates on tablets or smartphones.
-
Great for food trucks, pop-up shops, or on-the-go businesses.
-
Low setup costs and high flexibility.
4. Self-Service Kiosks
-
Customers place orders and pay without staff assistance.
-
Common in fast-food chains, cinemas, and airports.
5. Multichannel or Omnichannel POS
-
Integrates online and offline sales.
-
Let’s businesses track inventory across physical stores and e-commerce platforms.
POS in Different Industries
Retail
-
Fast barcode scanning, discount management, and returns processing.
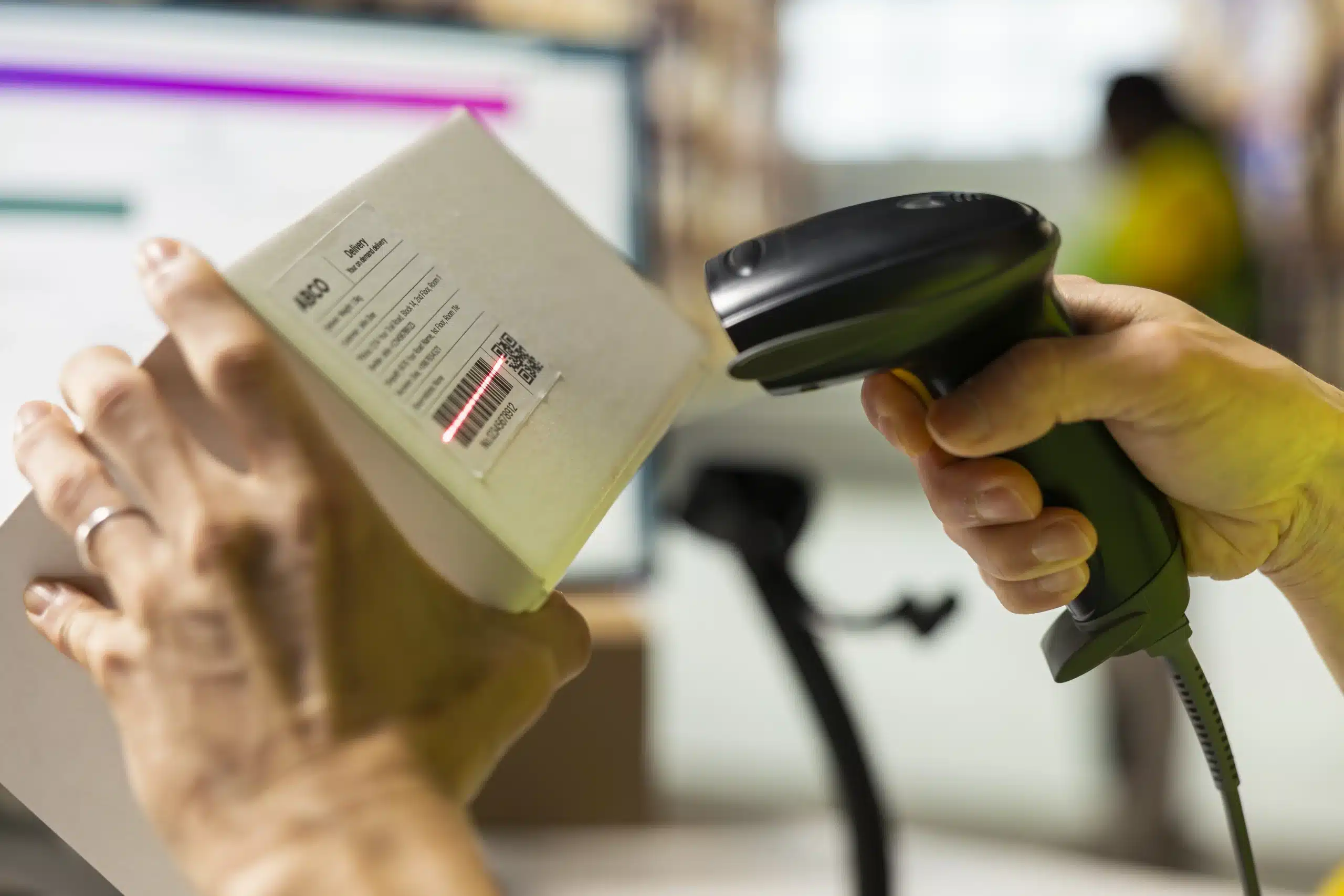

-
Tracks best-selling products and customer buying patterns.
Restaurants and Cafés
-
Table management, menu customization, and tip processing.
-
Kitchen display systems connect orders directly to chefs.
Hospitality
-
Hotels use POS to integrate restaurant, bar, and room charges.
-
Guest billing and loyalty programs tie into the system.
Healthcare and Services
-
Clinics use POS to manage appointments, billing, and inventory for supplies.
-
Gyms, salons, and spas rely on it for memberships and bookings.
Key Features to Look For in a POS
When choosing a POS system, business owners should consider:
-
Ease of Use – Staff should be able to learn quickly.
-
Payment Flexibility – Must support cash, cards, digital wallets, and contactless methods.
-
Inventory Tools – Automatic updates when items sell.
-
Offline Mode – Keeps working even without internet access.
-
Security – PCI-compliant systems that encrypt payment data.
-
Scalability – Ability to handle growth and multiple locations.
-
Customer Management – Tools for loyalty programs, discounts, and personalized offers.
The Future of Point of Sale
Technology continues to reshape how businesses handle transactions. Here are some emerging trends:
-
AI and Machine Learning: Predicting customer preferences, automating inventory orders.
-
Contactless Payments: Tap-to-pay, QR codes, and mobile wallets are becoming standard.
-
Biometric Authentication: Face recognition or fingerprints for secure payments.
-
Integration with E-commerce: Unified systems for online and in-person shopping.
-
Voice-Activated POS: Hands-free commands for faster service.
-
Blockchain and Crypto: Some businesses are exploring cryptocurrency payments.
The POS of the future won’t just process sales—it will serve as a full business intelligence hub.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits
-
Saves time with automated processes.
-
Improves customer satisfaction.
-
Enhances decision-making with real-time analytics.
-
Reduces errors in accounting and stock management.
Challenges
-
Cost: Advanced systems may be expensive upfront.
-
Internet Dependence: Cloud systems require reliable connectivity.
-
Security Risks: Sensitive data must be protected from cyber threats.
-
Training: Staff may need time to adapt to new systems.
How to Choose the Right POS System
If you’re a business owner, here are the steps to guide your decision:
-
Define Your Needs – Retail and restaurants require different features.
-
Set a Budget – Consider hardware, software, and monthly fees.
-
Check Compatibility – Make sure it works with your payment providers and devices.
-
Look for Integrations – Ensure it connects with your accounting and e-commerce platforms.
-
Read Reviews – Learn from other businesses in your industry.
-
Test Before Buying – Many providers offer free trials.
Real-World Examples
-
Square: Popular with small businesses for its ease of use and mobile flexibility.
-
Shopify POS: Integrates seamlessly with online stores.

-
Toast: Tailored for restaurants with strong menu and order management tools.
-
Lightspeed: Known for advanced inventory and reporting.
These examples show how different POS systems specialize in different industries.
Conclusion
The point of sale has evolved from a simple cash register to a sophisticated digital platform that manages sales, customers, and data. For businesses, choosing the right POS system is crucial for efficiency, customer satisfaction, and long-term growth.
Whether you run a local café, a bustling retail shop, or an online store, the POS is where your business meets your customer. And in today’s competitive environment, having the right system in place can turn each transaction into an opportunity for success.









 Samapak Food Industry is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Sama Pak Food is the webshop where you can find all your care products. The webshop was founded after customers from both at home and abroad asked us if we could send the products to them.
Samapak Food Industry is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Sama Pak Food is the webshop where you can find all your care products. The webshop was founded after customers from both at home and abroad asked us if we could send the products to them. Alkaram Foam is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. Alkaram Foam is a name of quality, luxury, and comfort. We offer foam mattress, spring mattress and medicated mattress at market-beating prices. Also, we make EPE foam rolls (Jumbolon rolls) and EPE shells (Jumbolon shells) for businesses.
Alkaram Foam is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. Alkaram Foam is a name of quality, luxury, and comfort. We offer foam mattress, spring mattress and medicated mattress at market-beating prices. Also, we make EPE foam rolls (Jumbolon rolls) and EPE shells (Jumbolon shells) for businesses. Al Noor Rice Corporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. AL NOOR provides the best quality of Rice to its customers all over Pakistan and the Rest of the World. We are renowned for producing different varieties of Basmati like Super Basmati Rice, 1121 Basmati Rice, 1509 Basmati Rice, and various categories of non-Basmati rice like C9, 386, irri-6 and irri-9.
Al Noor Rice Corporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. AL NOOR provides the best quality of Rice to its customers all over Pakistan and the Rest of the World. We are renowned for producing different varieties of Basmati like Super Basmati Rice, 1121 Basmati Rice, 1509 Basmati Rice, and various categories of non-Basmati rice like C9, 386, irri-6 and irri-9.



 Skye VIP Cars is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. It offers all kinds of car services in Dubai and all over the UAE, pleasing our clients to the highest level.
Skye VIP Cars is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. It offers all kinds of car services in Dubai and all over the UAE, pleasing our clients to the highest level. Delta Wye Power Incorporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Delta Wye Power Inc., another company he is involved with, focuses on medium-voltage transformers.
Delta Wye Power Incorporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Delta Wye Power Inc., another company he is involved with, focuses on medium-voltage transformers. County Public High School is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. CPS Gujrat has been set up to provide a sound education to the students with special emphasis on character building and the development of a wholesome personality. We aim to build the student’s power of judgment and appraisal of evidence by reasoning and inference.
County Public High School is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. CPS Gujrat has been set up to provide a sound education to the students with special emphasis on character building and the development of a wholesome personality. We aim to build the student’s power of judgment and appraisal of evidence by reasoning and inference. Cancer Patients Welfare Society GINUM is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The ultimate goal of CPWS GINUM is to help the ailing humanity of Cancer disease. CPWS helps cancer patients by providing free medicines and diagnostic facilities. In addition, CPWS helps GINUM administration in all aspects for the benefit of patients.
Cancer Patients Welfare Society GINUM is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The ultimate goal of CPWS GINUM is to help the ailing humanity of Cancer disease. CPWS helps cancer patients by providing free medicines and diagnostic facilities. In addition, CPWS helps GINUM administration in all aspects for the benefit of patients. Al-Huda Rice Mills is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS.
Al-Huda Rice Mills is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. 

 Ayk Trading Ltd. is one of the best landing page websites of PMS. Their Success is driven by the workforce & their Commitment to getting Results in the Right Way by Operating Responsibly, Executing with Excellence, and Applying Innovative Technologies and capturing New Opportunities for Development.
Ayk Trading Ltd. is one of the best landing page websites of PMS. Their Success is driven by the workforce & their Commitment to getting Results in the Right Way by Operating Responsibly, Executing with Excellence, and Applying Innovative Technologies and capturing New Opportunities for Development. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation was founded in 2015 with a vision to import and export ferrous and nonferrous metals in particular Aluminium. The aluminum business is inherited from us from our parent company and we continue to trade in other ferrous and nonferrous metals.
Qasim Iftikhar Corporation is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation was founded in 2015 with a vision to import and export ferrous and nonferrous metals in particular Aluminium. The aluminum business is inherited from us from our parent company and we continue to trade in other ferrous and nonferrous metals. Private Hospital Association Gujranwala is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The idea of a Private Hospital Association was the brainchild of Dr. Asif Ali Chaudhry, a renowned GP of Gujranwala, and his son Dr. Asad Ali Chaudhry, a prominent Gastro-Entrologist of our city, in view of an ever-increasing trend of medico-legal cases against private hospitals in this city.
Private Hospital Association Gujranwala is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The idea of a Private Hospital Association was the brainchild of Dr. Asif Ali Chaudhry, a renowned GP of Gujranwala, and his son Dr. Asad Ali Chaudhry, a prominent Gastro-Entrologist of our city, in view of an ever-increasing trend of medico-legal cases against private hospitals in this city. GMT (Pvt.)Ltd. is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. GMT Hearing Center is a Pakistani-based organization established in 2005. The purpose of the organization is to work for hearing, speech, physical and visual impairment.
GMT (Pvt.)Ltd. is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. GMT Hearing Center is a Pakistani-based organization established in 2005. The purpose of the organization is to work for hearing, speech, physical and visual impairment. Sami Goods Transport is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Sami Goods Transport (Pvt.)Ltd. has the vision to utilize the latest means of technology to provide swift and reliable Logistics solutions that provide Ease to our clients.
Sami Goods Transport is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Sami Goods Transport (Pvt.)Ltd. has the vision to utilize the latest means of technology to provide swift and reliable Logistics solutions that provide Ease to our clients. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PMSTTC. It has inspired students to become ethical leaders who lead lives significantly in services. It provides a way to get the technical training that you want according to your domain.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PMSTTC. It has inspired students to become ethical leaders who lead lives significantly in services. It provides a way to get the technical training that you want according to your domain.












 PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PTCL. Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL) a subsidiary of e& is the largest integrated Information Communication Technology (ICT) company in Pakistan.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PTCL. Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL) a subsidiary of e& is the largest integrated Information Communication Technology (ICT) company in Pakistan. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with DCN. DCN focuses on the data communication field with full product lines, including Switch, Wireless, Router, Security firewall and gateway, storage, CPE, and Cloud services.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with DCN. DCN focuses on the data communication field with full product lines, including Switch, Wireless, Router, Security firewall and gateway, storage, CPE, and Cloud services. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Poly. Poly is the leader in video and voice solutions. Learn how our technology can help your organization unleash the power of team collaboration.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Poly. Poly is the leader in video and voice solutions. Learn how our technology can help your organization unleash the power of team collaboration. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Dell Technologies. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Dell Technologies. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Hewlett-Packard. HP (Hewlett-Packard) is a multinational information technology (IT) company that sells hardware, software, and related business services.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Hewlett-Packard. HP (Hewlett-Packard) is a multinational information technology (IT) company that sells hardware, software, and related business services.
 At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Royal Bio Fuel. It is a Trading Web-based Application. The main features of the Trading System are as follows:
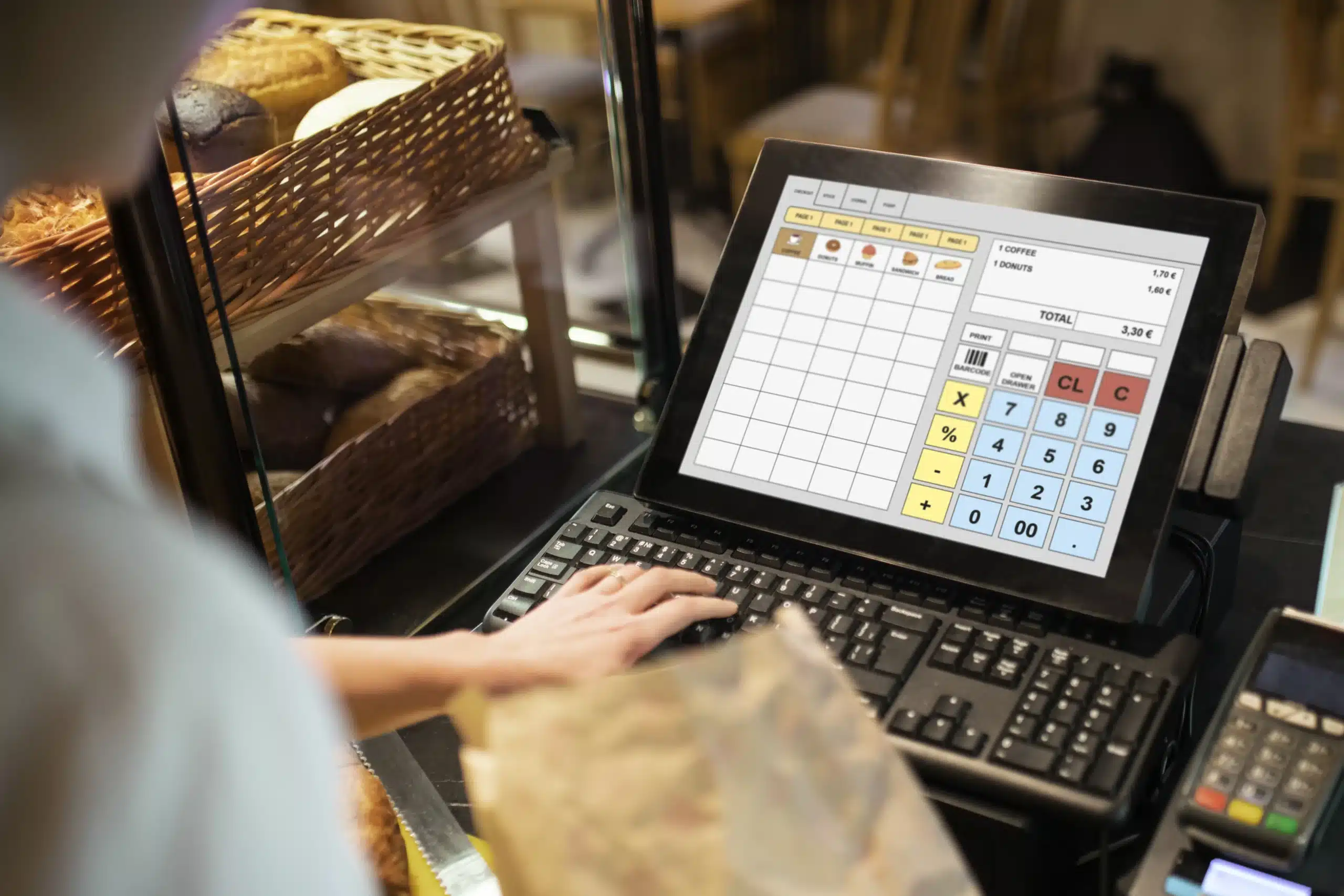
At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Royal Bio Fuel. It is a Trading Web-based Application. The main features of the Trading System are as follows: At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Pehalwaan Rewri. It is a Point Sale Web-Based Application. The main features of the Point of Sale System are as follows:
At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Pehalwaan Rewri. It is a Point Sale Web-Based Application. The main features of the Point of Sale System are as follows: PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Microsoft Partner Network. The Cloud Partner Program is how you build quickly, scale growth, sell worldwide, and stand out—all with a partner you can trust. No matter your goals, we’ll help you reach them.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Microsoft Partner Network. The Cloud Partner Program is how you build quickly, scale growth, sell worldwide, and stand out—all with a partner you can trust. No matter your goals, we’ll help you reach them. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Kaspersky. Grow your business – by partnering with a world leader. We provide the tools, incentives, and support to help you take your business to the next level. Across the world, Kaspersky is recognized for its innovative security solutions.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Kaspersky. Grow your business – by partnering with a world leader. We provide the tools, incentives, and support to help you take your business to the next level. Across the world, Kaspersky is recognized for its innovative security solutions. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its membership with SAP. Partners drive customer success with solutions from SAP, delivering trusted advice and deep product knowledge. SAP partners help you get the most from your software while enabling a smooth deployment.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its membership with SAP. Partners drive customer success with solutions from SAP, delivering trusted advice and deep product knowledge. SAP partners help you get the most from your software while enabling a smooth deployment. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Oracle. Oracle’s Partner ecosystem is critical to our customer’s success. Their differentiated services, combined with Oracle’s technology, help enable our customers to achieve their business goals.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Oracle. Oracle’s Partner ecosystem is critical to our customer’s success. Their differentiated services, combined with Oracle’s technology, help enable our customers to achieve their business goals.

 PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with ACTi. ACTi provides the full range of surveillance products – IP cameras, video management systems, TV wall systems, mobile applications, IoT devices, and access control systems.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with ACTi. ACTi provides the full range of surveillance products – IP cameras, video management systems, TV wall systems, mobile applications, IoT devices, and access control systems. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Longse. Longse focuses on comprehensive security and smart solutions. The product lines include HD Cameras, IP Cameras, Consumer Cameras, Access Control, Recorders, Accessories, Client Software, and apps.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Longse. Longse focuses on comprehensive security and smart solutions. The product lines include HD Cameras, IP Cameras, Consumer Cameras, Access Control, Recorders, Accessories, Client Software, and apps. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Fortinet. The Fortinet Security Fabric Platform delivers broad, integrated, and automated protections across the entire digital attack surface, securing critical devices, data, applications, and connections.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Fortinet. The Fortinet Security Fabric Platform delivers broad, integrated, and automated protections across the entire digital attack surface, securing critical devices, data, applications, and connections. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Planet. PLANET Technology Corporation is a leading global provider of IP-based networking products and solutions for small-to-medium-sized businesses, enterprises,
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Planet. PLANET Technology Corporation is a leading global provider of IP-based networking products and solutions for small-to-medium-sized businesses, enterprises, Sunny Flour Mills is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. The website has a different section that contains the details about company products. The end user can easily update products. SUNNY Group is a successful brand that has been milling wheat for 55 years. Sunny offers products that can appeal to the necessities of the giant baking experts in Pakistan.
Sunny Flour Mills is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. The website has a different section that contains the details about company products. The end user can easily update products. SUNNY Group is a successful brand that has been milling wheat for 55 years. Sunny offers products that can appeal to the necessities of the giant baking experts in Pakistan. PARSA Trust is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. PARSA Trust is a registered Not-For-Profit company established to aid hepatitis elimination efforts in Pakistan. At PARSA, the vision is to serve everyone and ensure quality treatment.
PARSA Trust is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. PARSA Trust is a registered Not-For-Profit company established to aid hepatitis elimination efforts in Pakistan. At PARSA, the vision is to serve everyone and ensure quality treatment. Trepak International is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. Trepak designs, develops and sells machines, aseptic packaging lines, and aseptic packaging material and also supplies installation planning and technical support.
Trepak International is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. Trepak designs, develops and sells machines, aseptic packaging lines, and aseptic packaging material and also supplies installation planning and technical support. Trace Engineering is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. TEC is primarily engaged in Power Generation, Transmission Lines, Substations, Distribution and Industrial Power Equipment, and the Hydel Sector of Pakistan.
Trace Engineering is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. TEC is primarily engaged in Power Generation, Transmission Lines, Substations, Distribution and Industrial Power Equipment, and the Hydel Sector of Pakistan. Used Sweden Machines Buy and sell Used Tetra Pak Filling Machines, Processing Equipments, and Spare Parts (UHT Plants, Pasteurizer, Homogenizers, and Aseptic Tanks). We specialize in consulting, planning, and supplying machines and complete systems for the processing and filling of liquid food and beverages.
Used Sweden Machines Buy and sell Used Tetra Pak Filling Machines, Processing Equipments, and Spare Parts (UHT Plants, Pasteurizer, Homogenizers, and Aseptic Tanks). We specialize in consulting, planning, and supplying machines and complete systems for the processing and filling of liquid food and beverages. Agrotech Food Industry is one of the best e-commerce websites of PMS. It provides Pure and healthy Food Ingredients and offers an extensive line of Superior pure spices, custom blended seasonings, and a wide variety of other specialty food ingredients.
Agrotech Food Industry is one of the best e-commerce websites of PMS. It provides Pure and healthy Food Ingredients and offers an extensive line of Superior pure spices, custom blended seasonings, and a wide variety of other specialty food ingredients. Obuy.pk is one of the satisfied e-commerce websites of PMS. It is an online shopping WordPress site with a wide range of Seller Services and tools that help creative entrepreneurs start, manage, and scale their businesses. About us, within our markets, millions of people around the world connect, both online and offline, to make, sell, and buy unique goods.
Obuy.pk is one of the satisfied e-commerce websites of PMS. It is an online shopping WordPress site with a wide range of Seller Services and tools that help creative entrepreneurs start, manage, and scale their businesses. About us, within our markets, millions of people around the world connect, both online and offline, to make, sell, and buy unique goods.
