In today’s interconnected world, information and communication technology is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Whether in business, education, healthcare, or government, digital systems form the backbone that powers communication, collaboration, and innovation. From the devices we use to access the internet to the complex networks that connect organizations globally, technology enables seamless information flow and efficient operations.
This article provides a detailed look at what ICT infrastructure is, why it matters, its main components, benefits, challenges, and the future trends shaping the digital landscape.

What is ICT Infrastructure?
It refers to the collection of hardware, software, networks, data centers, and services required to deliver information and communication capabilities within an organization or community. In simple terms, it is the foundation that supports computing, storage, communication, and data management.
Just as roads, bridges, and utilities are essential for a city’s physical growth, digital infrastructure is essential for modern growth. Without reliable systems, services such as online banking, e-learning, cloud computing, and e-governance would not function effectively.
Key Components
Although broad in scope, the structure can be broken down into several interconnected elements:
1. Hardware
Physical devices are the building blocks, including:
-
Servers for data storage and applications.
-
Computers and Laptops for everyday access.
-
Mobile Devices for remote communication.
-
Networking Devices like routers, switches, and firewalls.
-
Data centres are equipped with large-scale computing power.
2. Software
Programs that allow hardware to function:
-
Operating Systems such as Windows or Linux.
-
Enterprise Applications like ERP and CRM.
-
Middleware for system integration.
-
Security Tools for protection against cyber threats.
3. Networks
Connectivity is at the heart of the system:
-
LANs for offices and campuses.
-
WANs for global reach.
-
Wireless (Wi-Fi, 5G) for mobility.
-
The Internet is the global backbone.
4. Data and Storage Systems
Reliable storage solutions include:
-
On-premises servers and NAS.
-
Cloud-based storage for flexibility.
-
Backup and recovery systems to avoid data loss.
5. Skilled Professionals
Behind every system are IT experts—engineers, administrators, analysts, and security specialists—who manage and maintain operations.
Why It Matters
Its significance can be seen across multiple sectors:
-
Business: Supports communication, e-commerce, and decision-making.
-
Education: Enables e-learning, virtual classrooms, and digital libraries.
-
Healthcare: Powers electronic health records and telemedicine.
-
Government: Drives e-governance, smart cities, and digital taxation.
-
Society: Facilitates digital banking, payments, and entertainment.
Benefits
Investing in strong systems offers multiple advantages:
-
Higher Productivity through automation.
-
Cost Efficiency with cloud and virtualization.
-
Scalability to support growth.
-
Global Connectivity for businesses and individuals.
-
Innovation through AI, IoT, and blockchain.
-
Resilience with disaster recovery and cybersecurity.

Challenges
Despite the benefits, organizations face challenges such as:
-
High Costs of setting up advanced facilities.
-
Cybersecurity Threats like hacking and ransomware.
-
Rapid Technological Change requires frequent upgrades.
-
Skill Shortages in Managing Complex Systems.
-
Digital Divide between urban and rural areas.
Role of Cloud Computing
Cloud services have reshaped how organizations approach digital systems:
-
IaaS provides virtualized resources.
-
PaaS offers platforms for development.
-
SaaS delivers applications over the internet.
Hybrid and multi-cloud models allow flexibility, scalability, and reduced costs compared to traditional setups.
Security Considerations
As systems expand, so do risks. Effective protection requires:
-
Firewalls, encryption, and monitoring tools.
-
Regular updates and patches.
-
Employee training.
-
Compliance with data protection regulations.
Security builds trust and ensures continuity.
Impact in Developing Countries
Nations are investing in connectivity, broadband, and digital literacy to improve social and economic growth. However, challenges such as poor access and limited resources remain. Bridging the digital divide is key to sustainable development.
Future Trends
Several innovations are shaping the future:
-
5G and Beyond for faster connectivity.
-
Artificial Intelligence to optimize data centers and processes.
-
Edge Computing for real-time applications.
-
Green Technology for energy efficiency.
-
Blockchain for transparent transactions.
-
Digital Twins for better planning and monitoring.
Best Practices
To build strong systems, organizations should:
-
Invest in scalable architectures.
-
Embrace cloud-first strategies.

-
Prioritize cybersecurity from the start.
-
Conduct regular audits and upgrades.
-
Train staff for evolving digital skills.
Conclusion
ICT infrastructure is the foundation of the digital economy, connecting people, businesses, and governments worldwide. It combines hardware, software, networks, storage, and skilled professionals to power modern services. Though challenges such as costs, skill shortages, and cybersecurity remain, innovations like AI, 5G, and cloud technology are paving the way for smarter and more resilient systems.
For organizations and societies, investing in strong digital foundations is not just about keeping up—it’s about driving growth, inclusion, and innovation in a rapidly changing world.
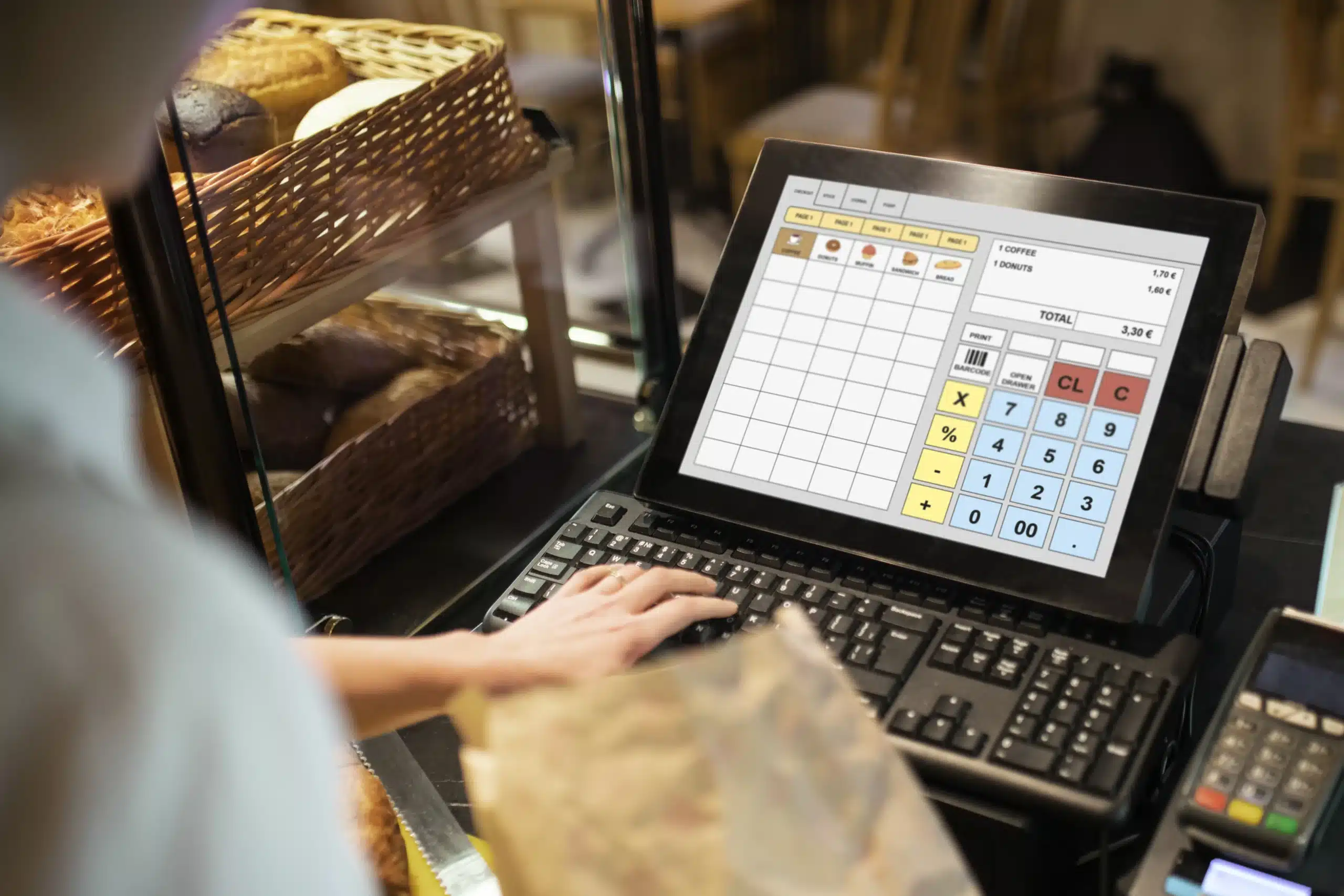









 Samapak Food Industry is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Sama Pak Food is the webshop where you can find all your care products. The webshop was founded after customers from both at home and abroad asked us if we could send the products to them.
Samapak Food Industry is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Sama Pak Food is the webshop where you can find all your care products. The webshop was founded after customers from both at home and abroad asked us if we could send the products to them. Alkaram Foam is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. Alkaram Foam is a name of quality, luxury, and comfort. We offer foam mattress, spring mattress and medicated mattress at market-beating prices. Also, we make EPE foam rolls (Jumbolon rolls) and EPE shells (Jumbolon shells) for businesses.
Alkaram Foam is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. Alkaram Foam is a name of quality, luxury, and comfort. We offer foam mattress, spring mattress and medicated mattress at market-beating prices. Also, we make EPE foam rolls (Jumbolon rolls) and EPE shells (Jumbolon shells) for businesses. Al Noor Rice Corporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. AL NOOR provides the best quality of Rice to its customers all over Pakistan and the Rest of the World. We are renowned for producing different varieties of Basmati like Super Basmati Rice, 1121 Basmati Rice, 1509 Basmati Rice, and various categories of non-Basmati rice like C9, 386, irri-6 and irri-9.
Al Noor Rice Corporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. AL NOOR provides the best quality of Rice to its customers all over Pakistan and the Rest of the World. We are renowned for producing different varieties of Basmati like Super Basmati Rice, 1121 Basmati Rice, 1509 Basmati Rice, and various categories of non-Basmati rice like C9, 386, irri-6 and irri-9.



 Skye VIP Cars is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. It offers all kinds of car services in Dubai and all over the UAE, pleasing our clients to the highest level.
Skye VIP Cars is one of PMS’s dynamic websites. It offers all kinds of car services in Dubai and all over the UAE, pleasing our clients to the highest level. Delta Wye Power Incorporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Delta Wye Power Inc., another company he is involved with, focuses on medium-voltage transformers.
Delta Wye Power Incorporation is one of PMS’s satisfied e-commerce websites. Delta Wye Power Inc., another company he is involved with, focuses on medium-voltage transformers. County Public High School is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. CPS Gujrat has been set up to provide a sound education to the students with special emphasis on character building and the development of a wholesome personality. We aim to build the student’s power of judgment and appraisal of evidence by reasoning and inference.
County Public High School is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. CPS Gujrat has been set up to provide a sound education to the students with special emphasis on character building and the development of a wholesome personality. We aim to build the student’s power of judgment and appraisal of evidence by reasoning and inference. Cancer Patients Welfare Society GINUM is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The ultimate goal of CPWS GINUM is to help the ailing humanity of Cancer disease. CPWS helps cancer patients by providing free medicines and diagnostic facilities. In addition, CPWS helps GINUM administration in all aspects for the benefit of patients.
Cancer Patients Welfare Society GINUM is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The ultimate goal of CPWS GINUM is to help the ailing humanity of Cancer disease. CPWS helps cancer patients by providing free medicines and diagnostic facilities. In addition, CPWS helps GINUM administration in all aspects for the benefit of patients. Al-Huda Rice Mills is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS.
Al-Huda Rice Mills is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. 

 Ayk Trading Ltd. is one of the best landing page websites of PMS. Their Success is driven by the workforce & their Commitment to getting Results in the Right Way by Operating Responsibly, Executing with Excellence, and Applying Innovative Technologies and capturing New Opportunities for Development.
Ayk Trading Ltd. is one of the best landing page websites of PMS. Their Success is driven by the workforce & their Commitment to getting Results in the Right Way by Operating Responsibly, Executing with Excellence, and Applying Innovative Technologies and capturing New Opportunities for Development. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation was founded in 2015 with a vision to import and export ferrous and nonferrous metals in particular Aluminium. The aluminum business is inherited from us from our parent company and we continue to trade in other ferrous and nonferrous metals.
Qasim Iftikhar Corporation is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Qasim Iftikhar Corporation was founded in 2015 with a vision to import and export ferrous and nonferrous metals in particular Aluminium. The aluminum business is inherited from us from our parent company and we continue to trade in other ferrous and nonferrous metals. Private Hospital Association Gujranwala is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The idea of a Private Hospital Association was the brainchild of Dr. Asif Ali Chaudhry, a renowned GP of Gujranwala, and his son Dr. Asad Ali Chaudhry, a prominent Gastro-Entrologist of our city, in view of an ever-increasing trend of medico-legal cases against private hospitals in this city.
Private Hospital Association Gujranwala is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. The idea of a Private Hospital Association was the brainchild of Dr. Asif Ali Chaudhry, a renowned GP of Gujranwala, and his son Dr. Asad Ali Chaudhry, a prominent Gastro-Entrologist of our city, in view of an ever-increasing trend of medico-legal cases against private hospitals in this city. GMT (Pvt.)Ltd. is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. GMT Hearing Center is a Pakistani-based organization established in 2005. The purpose of the organization is to work for hearing, speech, physical and visual impairment.
GMT (Pvt.)Ltd. is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. GMT Hearing Center is a Pakistani-based organization established in 2005. The purpose of the organization is to work for hearing, speech, physical and visual impairment. Sami Goods Transport is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Sami Goods Transport (Pvt.)Ltd. has the vision to utilize the latest means of technology to provide swift and reliable Logistics solutions that provide Ease to our clients.
Sami Goods Transport is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. Sami Goods Transport (Pvt.)Ltd. has the vision to utilize the latest means of technology to provide swift and reliable Logistics solutions that provide Ease to our clients. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PMSTTC. It has inspired students to become ethical leaders who lead lives significantly in services. It provides a way to get the technical training that you want according to your domain.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PMSTTC. It has inspired students to become ethical leaders who lead lives significantly in services. It provides a way to get the technical training that you want according to your domain.












 PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PTCL. Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL) a subsidiary of e& is the largest integrated Information Communication Technology (ICT) company in Pakistan.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with PTCL. Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL) a subsidiary of e& is the largest integrated Information Communication Technology (ICT) company in Pakistan. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with DCN. DCN focuses on the data communication field with full product lines, including Switch, Wireless, Router, Security firewall and gateway, storage, CPE, and Cloud services.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with DCN. DCN focuses on the data communication field with full product lines, including Switch, Wireless, Router, Security firewall and gateway, storage, CPE, and Cloud services. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Poly. Poly is the leader in video and voice solutions. Learn how our technology can help your organization unleash the power of team collaboration.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Poly. Poly is the leader in video and voice solutions. Learn how our technology can help your organization unleash the power of team collaboration. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Dell Technologies. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Dell Technologies. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Hewlett-Packard. HP (Hewlett-Packard) is a multinational information technology (IT) company that sells hardware, software, and related business services.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Hewlett-Packard. HP (Hewlett-Packard) is a multinational information technology (IT) company that sells hardware, software, and related business services.
 At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Royal Bio Fuel. It is a Trading Web-based Application. The main features of the Trading System are as follows:
At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Royal Bio Fuel. It is a Trading Web-based Application. The main features of the Trading System are as follows: At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Pehalwaan Rewri. It is a Point Sale Web-Based Application. The main features of the Point of Sale System are as follows:
At PMS (Pvt.)Ltd., we are dedicated to providing outstanding services to Pehalwaan Rewri. It is a Point Sale Web-Based Application. The main features of the Point of Sale System are as follows: PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Microsoft Partner Network. The Cloud Partner Program is how you build quickly, scale growth, sell worldwide, and stand out—all with a partner you can trust. No matter your goals, we’ll help you reach them.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Microsoft Partner Network. The Cloud Partner Program is how you build quickly, scale growth, sell worldwide, and stand out—all with a partner you can trust. No matter your goals, we’ll help you reach them. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Kaspersky. Grow your business – by partnering with a world leader. We provide the tools, incentives, and support to help you take your business to the next level. Across the world, Kaspersky is recognized for its innovative security solutions.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Kaspersky. Grow your business – by partnering with a world leader. We provide the tools, incentives, and support to help you take your business to the next level. Across the world, Kaspersky is recognized for its innovative security solutions. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its membership with SAP. Partners drive customer success with solutions from SAP, delivering trusted advice and deep product knowledge. SAP partners help you get the most from your software while enabling a smooth deployment.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its membership with SAP. Partners drive customer success with solutions from SAP, delivering trusted advice and deep product knowledge. SAP partners help you get the most from your software while enabling a smooth deployment. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Oracle. Oracle’s Partner ecosystem is critical to our customer’s success. Their differentiated services, combined with Oracle’s technology, help enable our customers to achieve their business goals.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Oracle. Oracle’s Partner ecosystem is critical to our customer’s success. Their differentiated services, combined with Oracle’s technology, help enable our customers to achieve their business goals.

 PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with ACTi. ACTi provides the full range of surveillance products – IP cameras, video management systems, TV wall systems, mobile applications, IoT devices, and access control systems.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with ACTi. ACTi provides the full range of surveillance products – IP cameras, video management systems, TV wall systems, mobile applications, IoT devices, and access control systems. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Longse. Longse focuses on comprehensive security and smart solutions. The product lines include HD Cameras, IP Cameras, Consumer Cameras, Access Control, Recorders, Accessories, Client Software, and apps.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Longse. Longse focuses on comprehensive security and smart solutions. The product lines include HD Cameras, IP Cameras, Consumer Cameras, Access Control, Recorders, Accessories, Client Software, and apps. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Fortinet. The Fortinet Security Fabric Platform delivers broad, integrated, and automated protections across the entire digital attack surface, securing critical devices, data, applications, and connections.
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Fortinet. The Fortinet Security Fabric Platform delivers broad, integrated, and automated protections across the entire digital attack surface, securing critical devices, data, applications, and connections. PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Planet. PLANET Technology Corporation is a leading global provider of IP-based networking products and solutions for small-to-medium-sized businesses, enterprises,
PMS (Pvt.)Ltd. is proud to announce its partnership with Planet. PLANET Technology Corporation is a leading global provider of IP-based networking products and solutions for small-to-medium-sized businesses, enterprises, Sunny Flour Mills is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. The website has a different section that contains the details about company products. The end user can easily update products. SUNNY Group is a successful brand that has been milling wheat for 55 years. Sunny offers products that can appeal to the necessities of the giant baking experts in Pakistan.
Sunny Flour Mills is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. The website has a different section that contains the details about company products. The end user can easily update products. SUNNY Group is a successful brand that has been milling wheat for 55 years. Sunny offers products that can appeal to the necessities of the giant baking experts in Pakistan. PARSA Trust is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. PARSA Trust is a registered Not-For-Profit company established to aid hepatitis elimination efforts in Pakistan. At PARSA, the vision is to serve everyone and ensure quality treatment.
PARSA Trust is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. PARSA Trust is a registered Not-For-Profit company established to aid hepatitis elimination efforts in Pakistan. At PARSA, the vision is to serve everyone and ensure quality treatment. Trepak International is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. Trepak designs, develops and sells machines, aseptic packaging lines, and aseptic packaging material and also supplies installation planning and technical support.
Trepak International is one of the satisfied dynamic websites of PMS. Trepak designs, develops and sells machines, aseptic packaging lines, and aseptic packaging material and also supplies installation planning and technical support. Trace Engineering is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. TEC is primarily engaged in Power Generation, Transmission Lines, Substations, Distribution and Industrial Power Equipment, and the Hydel Sector of Pakistan.
Trace Engineering is one of the best dynamic websites of PMS. TEC is primarily engaged in Power Generation, Transmission Lines, Substations, Distribution and Industrial Power Equipment, and the Hydel Sector of Pakistan. Used Sweden Machines Buy and sell Used Tetra Pak Filling Machines, Processing Equipments, and Spare Parts (UHT Plants, Pasteurizer, Homogenizers, and Aseptic Tanks). We specialize in consulting, planning, and supplying machines and complete systems for the processing and filling of liquid food and beverages.
Used Sweden Machines Buy and sell Used Tetra Pak Filling Machines, Processing Equipments, and Spare Parts (UHT Plants, Pasteurizer, Homogenizers, and Aseptic Tanks). We specialize in consulting, planning, and supplying machines and complete systems for the processing and filling of liquid food and beverages. Agrotech Food Industry is one of the best e-commerce websites of PMS. It provides Pure and healthy Food Ingredients and offers an extensive line of Superior pure spices, custom blended seasonings, and a wide variety of other specialty food ingredients.
Agrotech Food Industry is one of the best e-commerce websites of PMS. It provides Pure and healthy Food Ingredients and offers an extensive line of Superior pure spices, custom blended seasonings, and a wide variety of other specialty food ingredients. Obuy.pk is one of the satisfied e-commerce websites of PMS. It is an online shopping WordPress site with a wide range of Seller Services and tools that help creative entrepreneurs start, manage, and scale their businesses. About us, within our markets, millions of people around the world connect, both online and offline, to make, sell, and buy unique goods.
Obuy.pk is one of the satisfied e-commerce websites of PMS. It is an online shopping WordPress site with a wide range of Seller Services and tools that help creative entrepreneurs start, manage, and scale their businesses. About us, within our markets, millions of people around the world connect, both online and offline, to make, sell, and buy unique goods.
